Using dedicated relays for total connectivity
Relays help you reach total connectivity. Managed Nebula works on most network topologies out of the box with hole punching, a technique where both hosts work to open a direct connection with each other. Some networks though, don't have a path to direct connectivity between hosts. That's why Defined Networking built Relays, a feature that allows you to route traffic via special hosts called relays while still retaining end-to-end encryption between hosts.
Some examples of where you might need relays:
- You're behind a symmetric NAT that generates a unique IP:port for every unique host:port connection
- You're behind a CGNAT, often seen when connecting from a mobile device on cellular
Once you create your first lighthouse, you have a relay!
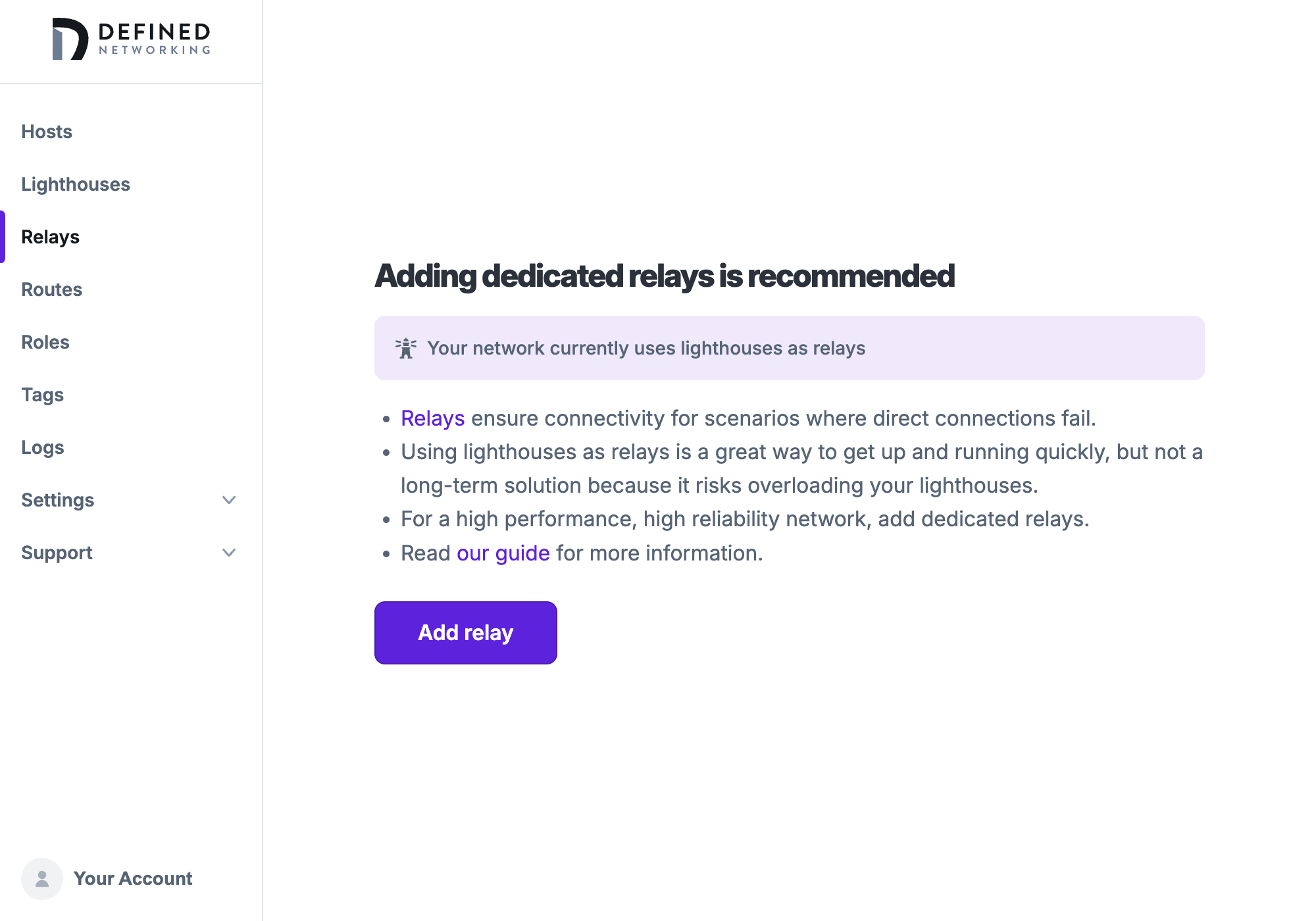
Relays page showing lighthouses are used as a relay, recommending dedicated relays.
This will allow hosts without direct connectivity to route through the lighthouse and ensure they can still communicate with other hosts on your network. Using lighthouses on your networks as relays is a stopgap measure to make setup of a Managed Nebula network easy, but as your network scales, it becomes important to separate concerns and host relays separately as dedicated relays.
Set up your first dedicated relay
Using lighthouses as relays is convenient, but it can add extra load to a critical part of your networking infrastructure. Creating dedicated relays moves that traffic to separate machines, improving the reliability of your network.
To set up a dedicated relay, go to the Relays page of the Admin Panel and begin adding a relay.
You'll need to choose which UDP port to serve the relay service on, similar to a lighthouse. The default is 4242, but any port can work.
Make sure the port has firewall rules on the host opened to the public internet, for example allowing 4242/udp.
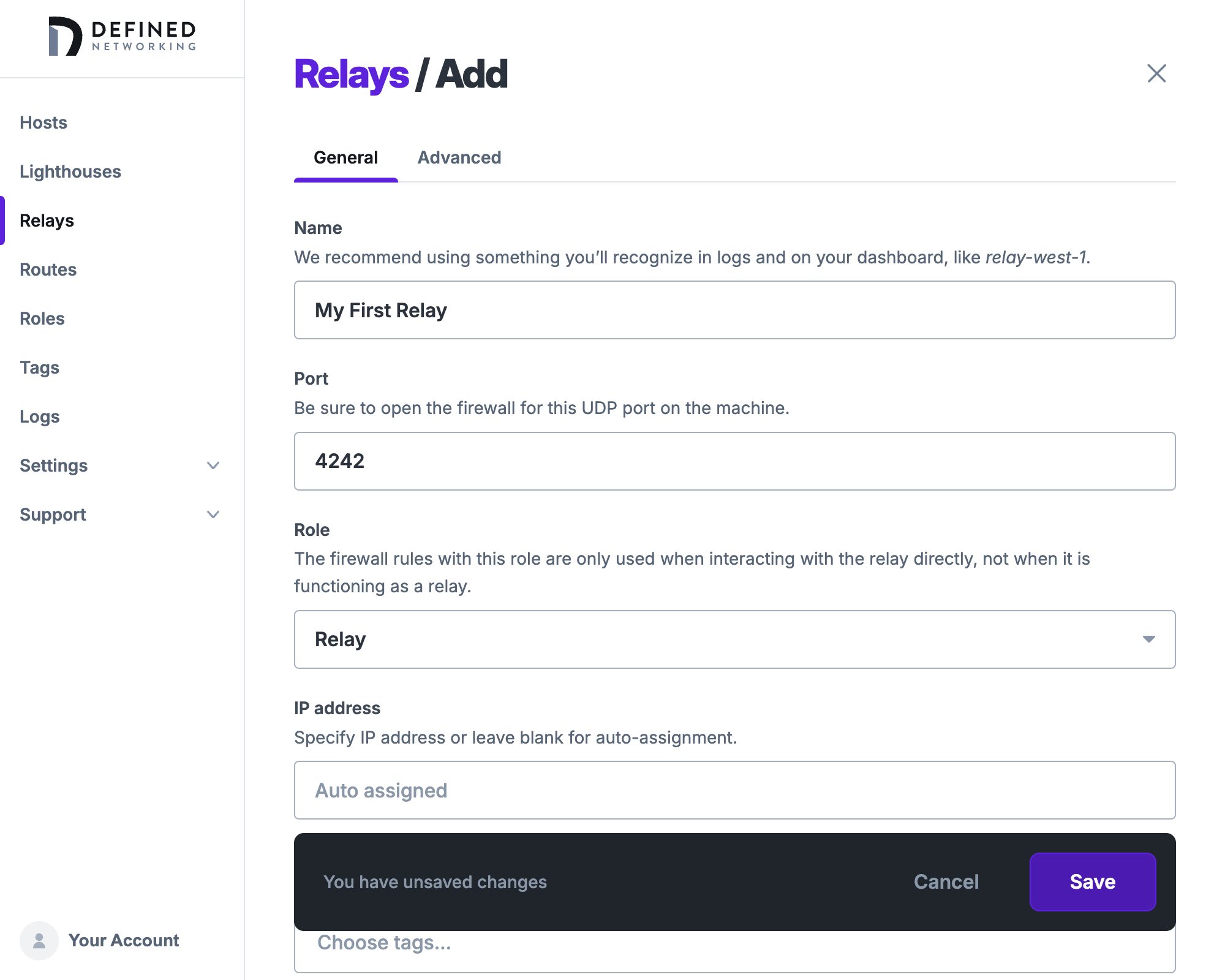
Add a new relay
You'll want to enroll your new relay on a machine that has the selected port opened directly to the internet. Once you do, you'll be able to see the relay in the relays page. If you can't enroll the host immediately, you can always go back later and select “re-enroll” for the host in the UI.
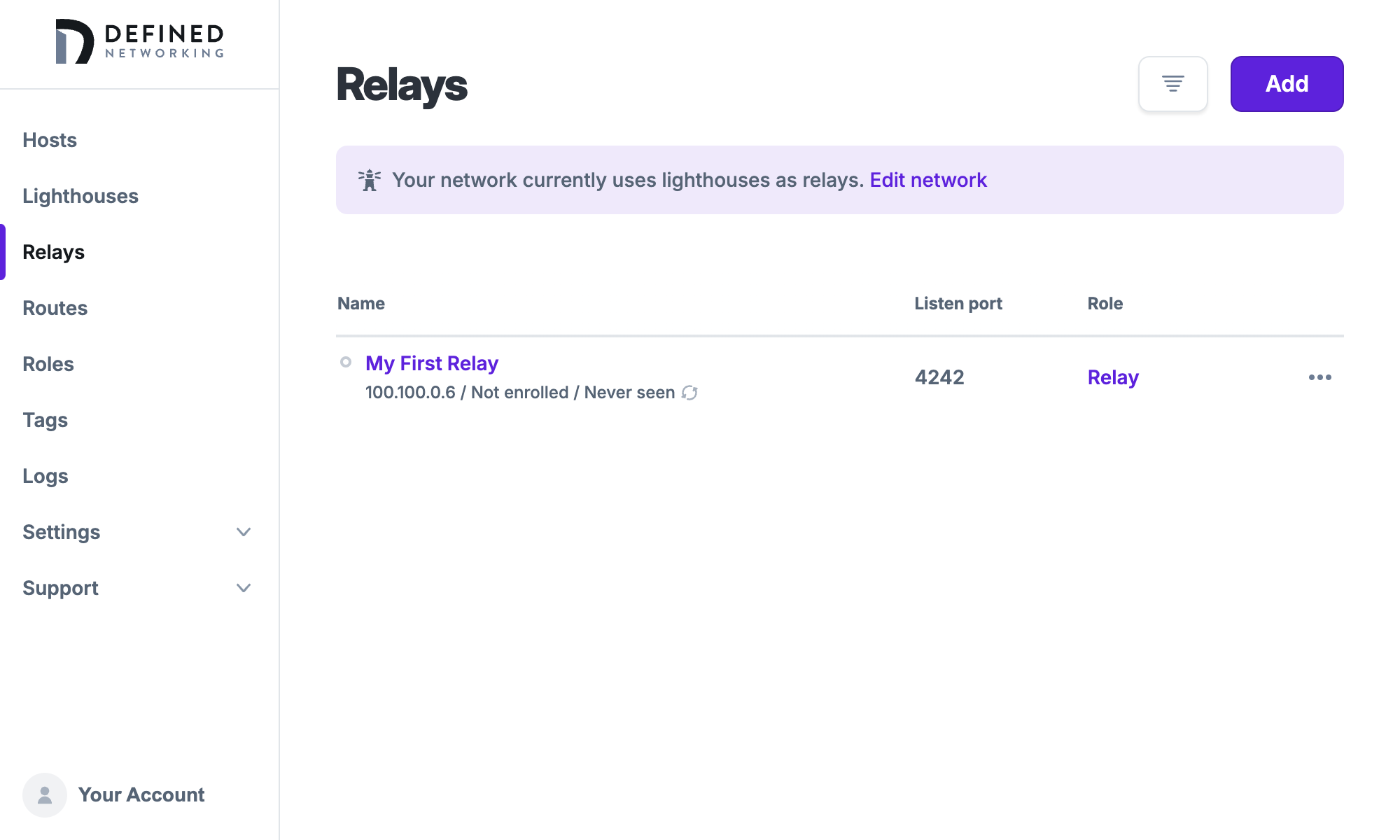
Once you've enrolled your Relay, you now have your lighthouses plus one dedicated relay offering relaying services to your hosts.
Using only dedicated relays
Once you've set up enough dedicated relays to handle your expected traffic, you should transition to only using dedicated relays.
To do so, click the "Edit network" button to visit the Settings -> Networks page. Click on the network name to edit the network, then uncheck the box that says "Use lighthouses as relays", and save the change.
Your lighthouses will no longer initiate new relay connections, though they will continue relaying messages over existing relay connections that were previously established.
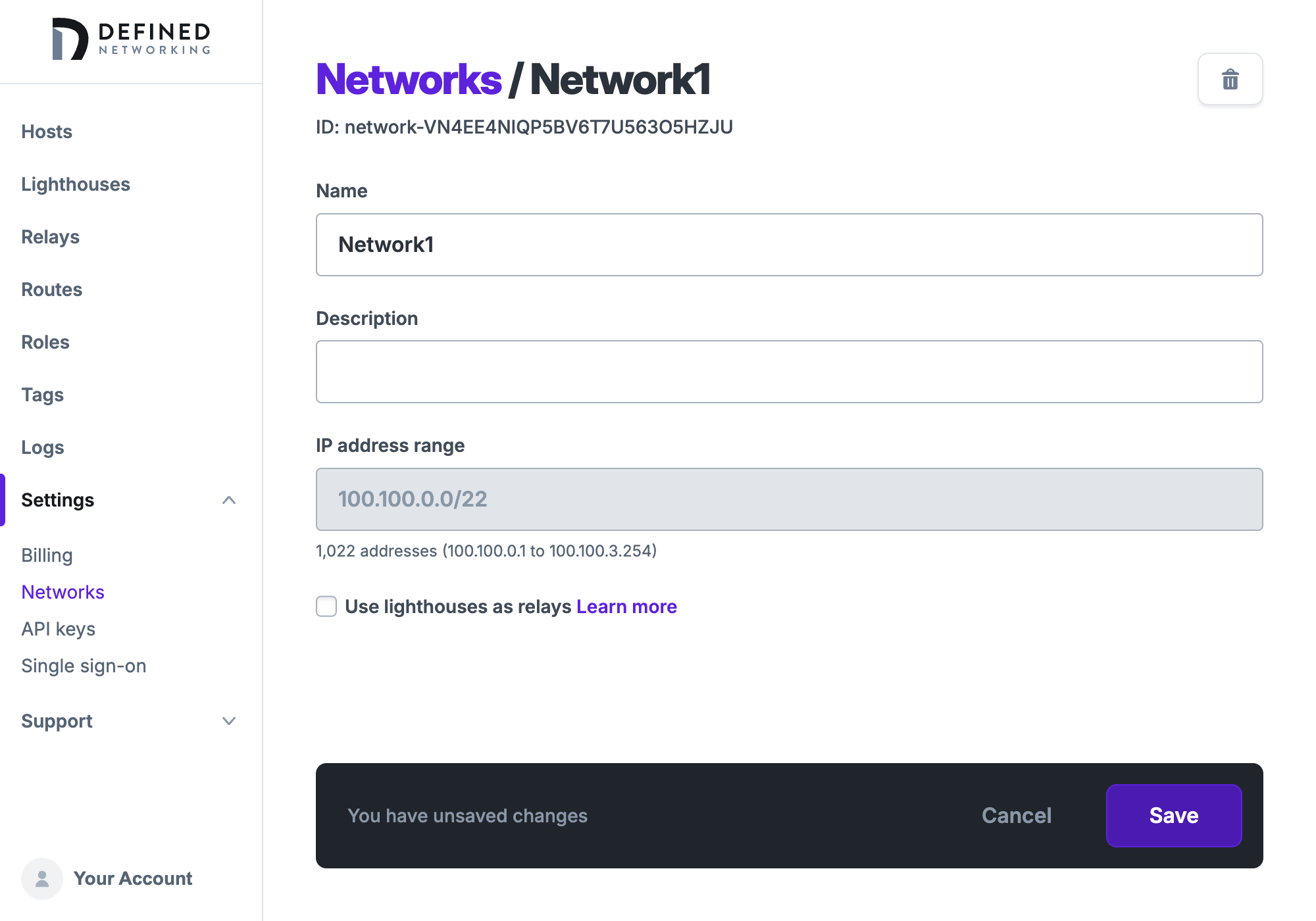
Since relays add an extra step in the traffic between nodes, it's a good idea to set up relays as geographically close to your other machines as possible.
For example, if you have hosts in AWS us-east-1 and us-west-2, you might create relays relay-us-east-1 and relay-us-east-2 that you host near their respective data centers.